Introduction
The Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) Volatility Index, commonly known as the VIX, is a widely tracked financial metric designed to measure the market’s expectations of short-term volatility. Often referred to as the “fear gauge,” the VIX is essential for both individual and institutional investors to understand market sentiment and potential risk. In this blog post, we will break down what the VIX is, how it moves, why it’s important, and how to use it to your advantage.
What is the VIX and what does it measure?
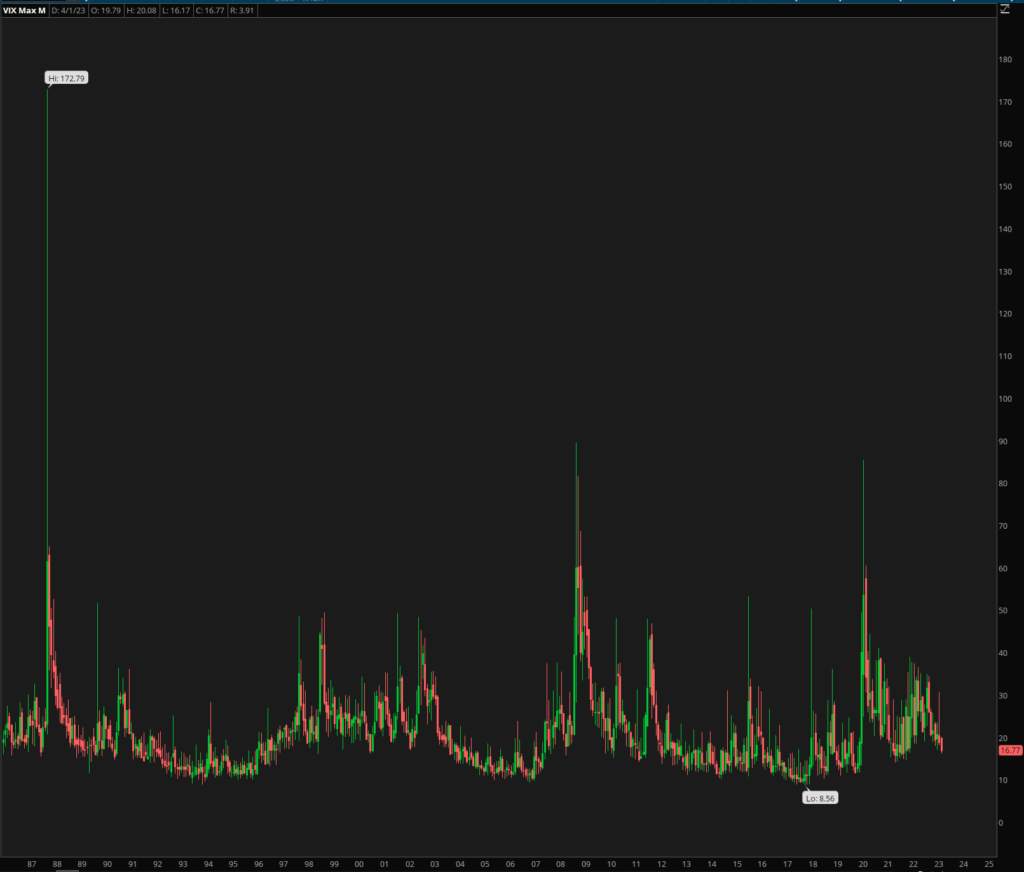
The VIX was introduced by the CBOE in 1993 as a real-time index to measure the market’s expectation of 30-day volatility. The index is calculated using the prices of near-term S&P 500 index options, both calls and puts, which are used to estimate the implied volatility of the market. In simple terms, the VIX gauges the market’s perceived likelihood of significant price swings in the near future.
How and why does the VIX move?
The VIX moves based on market participants’ expectations of future volatility, as reflected in option prices. When option prices increase, it typically indicates that investors are anticipating larger price swings and are thus willing to pay more for options as a form of protection. This results in a higher VIX value. Conversely, when option prices decrease, the VIX value will generally fall, as market participants expect less volatility.
Several factors can contribute to changes in the VIX, including:
- Economic data releases
- Political events
- Corporate earnings announcements
- Market sentiment shifts
Why is the VIX important?
The VIX serves as a valuable tool for gauging market sentiment and potential risk. Here are three key reasons why it’s important for investors:
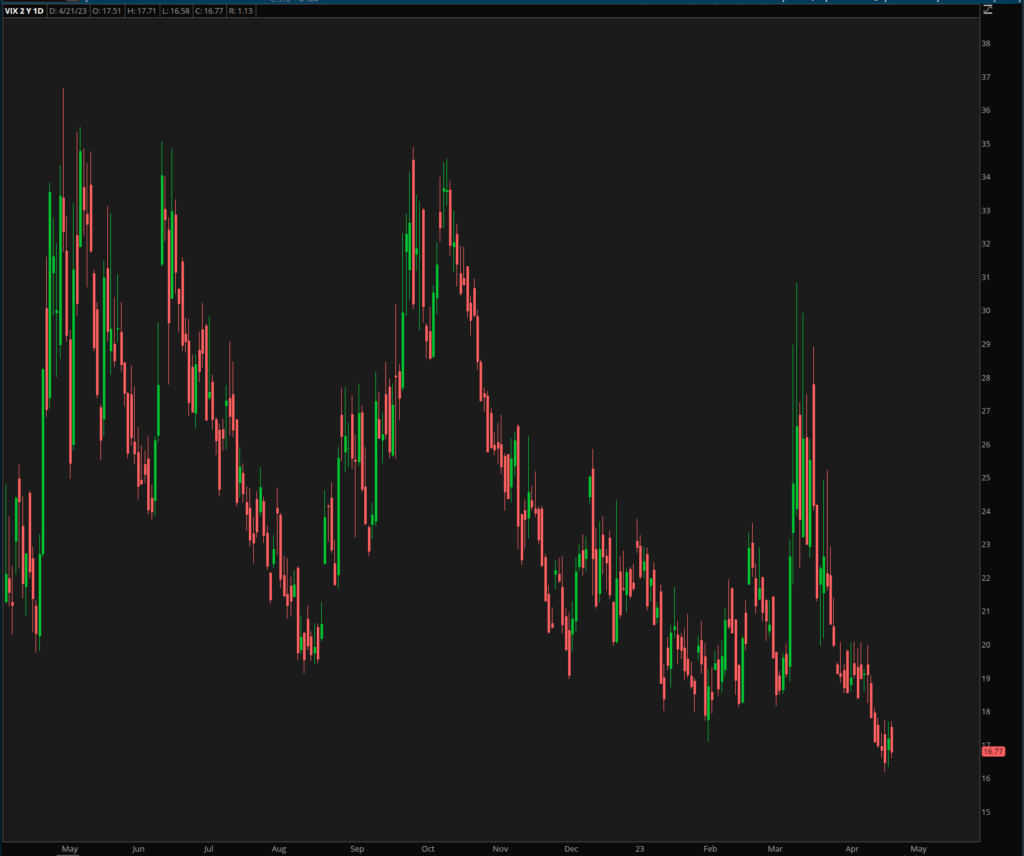
a) Market sentiment indicator: A high VIX value indicates heightened investor anxiety, while a low value suggests that market participants are more complacent. This insight can help investors understand the prevailing market mood and adjust their strategies accordingly.
b) Risk management: The VIX can be used to assess the overall risk level in the market, allowing investors to adjust their portfolios to better manage potential volatility.
c) Diversification: As the VIX tends to be inversely correlated with the S&P 500, it can provide a valuable diversification tool for investors looking to hedge their equity positions.
How to use the VIX to your advantage
While the VIX itself is not directly tradable, several financial products, such as futures, options, and exchange-traded notes (ETNs), are based on the index. Investors can use these products to implement various strategies, including:
a) Hedging: Investors can use VIX-based products to hedge against potential market downturns by taking advantage of the index’s inverse relationship with the S&P 500.
b) Speculation: Traders can use VIX derivatives to profit from anticipated changes in market volatility, either by going long when they expect the VIX to rise or short when they anticipate a decline.
c) Diversification: Adding VIX-based products to a portfolio can provide diversification benefits, as the index generally exhibits low correlation with other asset classes.
Conclusion
The CBOE Volatility Index (VIX) is a crucial financial metric that helps investors gauge market sentiment and potential risk. By understanding what the VIX measures and how it moves, investors can make more informed decisions and better manage their portfolios in a constantly changing market landscape.
If you found this article helpful, be sure to check out our other educational posts here! And be sure to sign up for our weekly newsletter where cover the market for free!


